BLEEDING GUMS
Gum bleeding is a common condition that most of us usually encounter. It is usually
noted while brushing or flossing. Bleeding gums are caused by inadequate plaque
removal and it will harden into calculus. It contains bacteria which attack the
healthy tissue around the teeth. This will cause the gums to become inflamed and
irritated. This is also a form of gum disease called as gingivitis. It is usually
characterized by swollen red gums along with halitosis or bad breath. This can be
reversed completely with proper treatment. Lack of treatment can lead to serious
condition called periodontitis that may result into tooth loss.
Diabetic patients and pregnant women also have gums that bleed easily and are more
prone to gum diseases. These group of people require frequent routine dental check-up
and prophylactic treatment to maintain healthy gums. Other causes may include some
medications like anticoagulants. Gum disease can also be associated with serious
conditions like bleeding disorder and even it can be a sign of blood cancer. So
it is important not to ignore bleeding gums. Persistent bleeding after the removal
of local factors should be noticed with outmost care.
ORAL CANCER
Oral cancers develop on the tongue, the tissue lining the mouth and gums, under
the tongue, at the base of the tongue, and the area of the throat at the back of
the mouth. Oral cancer most often occurs in people over the age of 40 . Most oral
cancers are related to tobacco use, alcohol use (or both), or infection by the human
papilloma virus (HPV). Most oral cancers show early changes in the oral cavity as
colour change or texture change or ulcer or swelling which are called potentially
malignant disorders. OMR specialists are trained in carrying out systematic clinical
examination of mouth as well essential chair side investigations which may help
to rule out malignancy.
So If you have any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, you need to consult
a OMR specialist.
A white or red patch in your mouth
A sore OR thick patch in your mouth, lip, or throat
A irritation or lump in your mouth, lip, or throat
- A feeling that something is caught in your throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Difficulty moving your jaw or tongue
- Swelling in your jaw
- Numbness in your tongue or other areas of your mouth
Remember all colour changes, swelling, ulcer etc in mouth are NOT CANCER. If you
are a smoker, use tobacco in any form, chew gutka or consume alcohol take extra
precaution and have periodic check up. Catch the cancer early.
PIGMENTATION
Pigmentation which do not require treatment
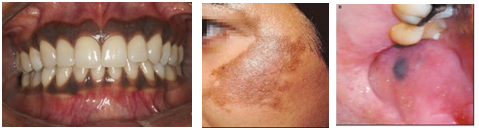
Pigmentation which require treatment

There are several conditions where discoloration is seen in mouth and it does not
require treatment. These discoluration can be normal or due to intake of some medicine
or due to smoking.
Discolouration can also be due to injuries leading to certain external particles
getting embedded such as broken off pencil points causing a gray colour (this is
most common in children). Certain medications and mouth rinses may also discolour
the tissue. Metal poisoning from bismuth, mercury, lead, silver, arsenic, copper,
and zinc which is normaly a contant of your tooth filling, and other dental materials
or daily used materials., can also cause blue, black, and grey streaks. Sometimes
injury to blood vessels can also cause blue to purple discoloration There are also
a wide range of conditions that can create brown to black discoloration, including
pregnancy, overactivity of the pituitary gland, chronic adrenal insufficiency
There are condition where pigmentation are seen in mouth which indicate systemic
condition or cancer, which cannot be differentiated normaly and has special feature.
To differentiate these discolouration ,it require oral physician consultation.
SWELLINGS IN MOUTH
Swellings in the mouth can originate in any type of tissue in an around the mouth,
including bone, muscles, and nerve. Swelling most commonly form on the
- Lips
- Sides of the tongue
- Floor of the mouth
- Back portion of the roof of the mouth (soft palate)
Causes for this growth can be,
- Noncancerous (benign)
- Precancerous (dysplastic)
- Cancerous (malignant)
Some of the swellings are absolutely normal structures in the mouth like circumvallate
papillae, accessory tonsilar tissue which may get confused with some disease and
does not require treatment ,while most of the mouth swellings are noncancerous like
tori (a bony expansion), and eupilis etc which need treatment if required, but,
Still there are mouth swellings which can be cancerous and require oral physician
consultation and immediate treatment, which include verrucous carcinoma, malignant
melanoma, minor salivary gland neoplasm etc.
Some of the growth which is not cancerous
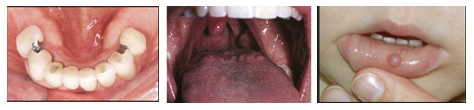
Some of the growth which is cancerous

Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
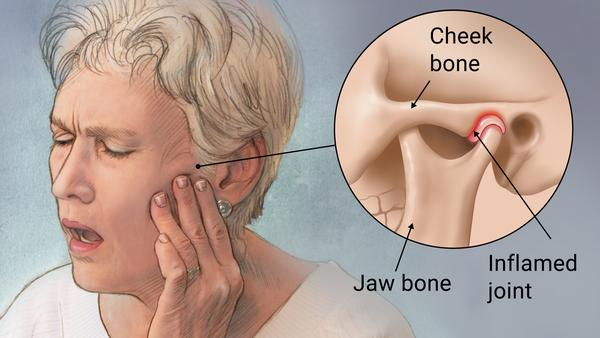
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the hinge joint that connects the lower jaw to the skull, which is immediately in front of the ear on each side of the head. Temporomandibular joint disorders occur as a result of problems with the jaw, jaw joint and surrounding facial muscles that control chewing and movement of the jaw. It can cause due to grinding of the teeth, unilateral chewing habit, erosion of the joint, arthritis, stress etc. The most common symptom of TMJ disorder is pain in the jaw and surrounding muscles. Other symptoms typically associated with these disorders include stiffness in the muscles of the jaw, limited movement of the jaw, locking of the jaw and clicking or popping sound from the TMJ site. TMJ pains are easily mistaken as headache or ear pain. Treatment of the TMJ pain include medications, dental corrections, night guard, stress counseling and other physical therapies like acupuncture, relaxation techniques, biofeedback etc. A thorough dental and TMJ examination by an oral medicine specialist is important for the proper diagnosis and management.